Article Text
Abstract
Background Non-compaction of the left ventricle (NCLV) is an unclassified cardiomyopathy due to intrauterine arrest of compaction of the loose interwoven meshwork. Only a few studies involving sub-Saharan Africans insmall numbers have been published. The aim of our study was to determine the diagnostic, therapeutic and prognostic aspects as well as the clinical course of NCLV in a black African population.
Methodology A multicentre retrospective study was carried out between November 2007 and June 2012 in two cardiology departments in Dakar. Patients who met the echocardiographic criteria for NCLV were included in the study.
Results 35patients with the diagnosis of NCLV were evaluated in the study. Their mean age was 47±18.4 years. Heart failure was found in 77.1% of the patients. The most frequent electrocardiographic abnormalities were left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) (46%) and sinus tachycardia (43%). Mean non-compaction/compaction ratio was 2.84±0.68 with preferential localization in the apex of the left ventricle. The main complications observed were cardiogenic shock (23.5%), pulmonary embolism (6.3%) and ventricular tachycardia (5.9%). Diuretics and ACE inhibitors were the medications most often prescribed. Age >60 years (p=0.04), male gender (p=0.03) and the occurrence of complications during follow-up (p=0.04) were noted to be predictors of poor prognosis.
Conclusion Contrary to previous beliefs, NCLV may not be less common in black Africans than in other ethnic subgroups. Clinicians in Africa should be made aware of NCLV so that it can be diagnosed at earlier stages.
- Isolated noncompaction of the left ventricular myocardium
- heart failure
- echocardiography
- Senegal
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Introduction
Non-compaction of the left ventricle (NCLV) is a rare congenital cardiomyopathy of recent description, belonging to the 'unclassified' group of cardiomyopathies according to the classification of the WHO.1 It is the consequence of an alteration of the structure of the myocardium, probably due to an arrest of compaction during intrauterine life.1 It is characterised anatomically by the presence of numerous prominent myocardial trabeculae with deep intertrabecular recesses communicating with the left ventricular cavity and without connection with the coronary artery.2–5 It is either isolated or associated with other cardiac or extracardiac abnormalities6 7 such as complex cyanotic heart disease, coronary artery congenital abnormalities, obstruction of the left or right ventricular chamber, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, atrioventricular duct and bicuspid aortic valve.8–13
The interest of our study lies in the apparent rarity of this disease and the near absence of African studies on this topic. Studies in black African subjects with small numbers have been rarely published.1 14 15 Peters et al were the first to publish a large prospective study, including 54 individuals all of African origin, that documented this condition.16 The aim of our study was to determine the diagnostic, therapeutic and evolutionary aspects of isolated left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy in sub-Saharan African adults.
Methodology
This is a retrospective, descriptive, and analytical study conducted over a 5-year period, from 1 November 2007 to 30 June 2012, in the cardiology departments of the General Hospital of Grand Yoff and the Aristide Le Dantec Hospital.
Patients in whom left ventricular non-compaction was detected on echocardiography were included in the study.
Diagnosis was made at echocardiography based on Jenni’s criteria as follows:
presence of multiple left ventricular trabeculae (>3);
presence of deep intertrabecular recesses;
visualisation of colour Doppler flow within the recess and in communication with the left ventricular cavity;
presence of a double layered endocardial structure with an uncompacted zone/compacted zone ratio >2 in end systole.
All these criteria had to be present to make the diagnosis. Dimensions of the cardiac chambers and thickness of the interventricular septum and posterior left ventricular wall were collated. Left ventricular systolic function was calculated using the Simpson biplane method. Systolic function of the right ventricle was assessed by measurement of the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE). Left ventricular filling pressures were evaluated. Pulmonary artery pressure was assessed at Doppler on the tricuspid insufficiency flow. The diameter of the inferior vena cava was measured. For the localization of the uncompacted zone, we used the 17-segment model of the left ventricle.
Complete clinical examination as well as measurement of biological parameters were undertaken; ECG, chest x-ray and cardiac MRI (if available) were also performed. A family screening was conducted for all first-degree relatives who freely accepted the screening. We also recorded the occurrence of complications and/or deaths as reported in the medical records to assess the evolution of the patients' condition.
The data collected were analysed using the Epi info version 3.5.3 software. The χ2 or Fisher test were used for the comparison of proportions and the analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal-Wallis H test for mean comparisons. A value of p<0.05 was considered as a threshold for statistical significance. The bivariate analysis made it possible to determine the factors of poor prognosis. The overall survival analysis was determined using the method of Kaplan-Meier.
Results
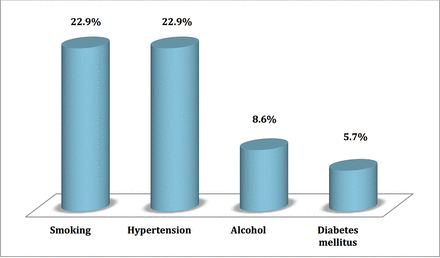
During the study period, 35 patients were recruited. The mean age was 47±18.4 years with a range of 19 to 82 years. The sex ratio was 1.69. Hypertension and smoking were each the most prevalent risk factors in eight cases (22.9%), as shown in figure 1.
Distribution of risk factors among the population.
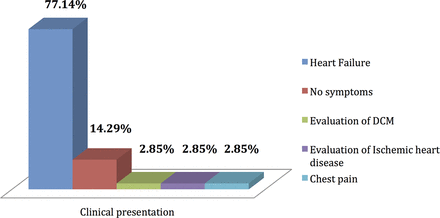
Heart failure was present in 77% of cases (figure 2) and 81% of patients were in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class IV. Table 1 shows distribution of symptoms among the population.
Clinical diagnosis at presentation. DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy.
Distribution of symptoms among population
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) was the most common ECG abnormality and was found in 46% of cases. Various conduction disorders were encountered: left bundle branch block in six cases (17.1%), anterior hemiblock in six cases (17.1%) and a high degree atrioventricular block associated with anterior hemiblock in one case. Heart rhythm disorders were dominated by sinus tachycardia in 15 cases (43%) and ventricular extrasystoles in eight cases (23%).
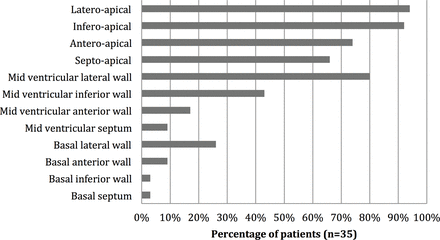
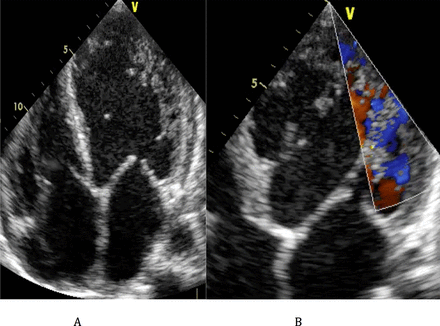
Mean ratio of uncompacted zone to compacted zone was 2.84±0.68 with a range of 2.20 to 5. The preferential localisation of NCLV was apical (figure 3). We found dilation of the left ventricle in 88% of cases and dilation of the left atrium in 63% of cases. The right ventricle was dilated in 54% of cases. There was diffuse hypokinesia in 91% of cases and septal dyskinesia in four cases (13%). Left ventricular systolic function was altered in 30 patients (85.7%) (table 2). Two patients (5.7%) had a thrombus in the left ventricle. Elevated left ventricular filling pressure was found in 75% of the cases. Table 3 shows the values of the different echocardiographic parameters, and figure 4 illustrates NCLV on an apical four-chamber echocardiographic view.
Distribution of patients according to the localisation of structural abnormalities.
(A) Apical four-chamber view of a left ventricular non-compaction with multiple trabeculations on septo-apical, latero-apical and mid lateral wall. (B) Flux penetrating the trabeculations with colour Doppler.
Distribution of left ventricular ejection fraction
Values of the echocardiographic parameters
Therapy was administered by the treating cardiologists: loop diuretics were prescribed in 29 cases (82.8%); 26 patients (74.3%) were on aldosterone antagonists; 30 patients (85.7%) received ACE inhibitors; 13 subjects (37.1%) were taking digitalis; 15 patients (42.9%) were on β-blockers; and vitamin K antagonists were administered to 26 patients (74.3%). One patient with a bi-fascicular block (anterior hemiblock associated with a high-level atrioventricular block) benefited from the placement of a pacemaker in the DDD mode.
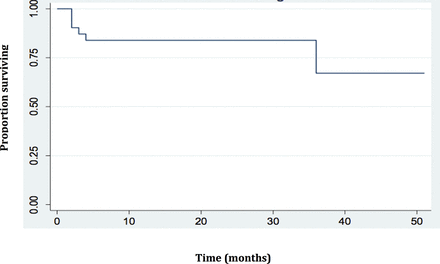
The duration of follow-up of our patients ranged from 2–51 months, with a mean of 17.2±14.5 months. Complications occurred in 17 patients. Acute heart failure was the most frequent complication (58.8%). Cardiogenic shock occured in 23.5% of patients, pulmonary embolism in 6.3% and ventricular tachycardia in 5.9% of patients. The mortality rate in our series was 20.6%; five deaths occurred before 10 months of follow-up. Figure 5 represents Kaplan-Meier plot of NCLV in our series. Factors for a poor prognosis were age >60 years (p=0.045), male gender (p=0.032) and complications occurring during the follow-up (p=0.043).
Kaplan-Meier plot of non-compaction of the left ventricle survival.
Twenty-three relatives underwent screening and five of them (21.7%) were diagnosed with NCLV. We found a recurrence risk of 67%.
Discussion
Isolated ventricular non-compaction is a rare congenital disorder that is categorised as an unclassified cardiomyopathy.1 Our series of 35 patients is the largest involving West Africans to date. Clinical and echocardiographic characteristics and outcomes during follow-up are reported.
In our series, mean age at diagnosis was 47±18.4 years, similar to that reported elsewhere in the literature. In the Paule series, involving three black African subjects, their ages were 23 years, 42 years and 45 years.1 The age at diagnosis of adult cases described in the literature is 40 years for Oechslin et al,17 52 years for Stöllberger et al 18 and 37 years for Murphy et al 19 in respective series involving 34, 86 and 45 adults.
The clinical manifestations of NCLV are not specific and the circumstances of diagnosis are multiple. The most frequently described clinical presentations are heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias and thromboembolic events.20 Also, the disease can be diagnosed after sudden death or as an incidental finding.21 In our study, the majority (81%) of our patients were diagnosed in stage IV NHYA. Indeed, the difficulty of accessing health facilities in general and specialised services in particular, combined with financial constraints, are often responsible for a considerable diagnostic delay. In the French register of NCLV, Habib et al reported a predominance of congestive heart failure at diagnosis in 43% of cases, followed by the evaluation of a DCM in 21%. Rhythm disorders were found in 11% of cases, family members were screened in 8% and embolic events occurred in 4%.22
The most common ECG abnormality in the Habib series was LVH (18%).22 Steffel reported LVH in 38% of the cases.23 Atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia in adult series ranged from 18–41%.17–19 In our series, a long-term electrocardiographic recording had been underused, explaining the low rate of ventricular tachycardia.
Echocardiography is used as a first-line examination for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with NCLV.5 17 How does the preferential localisation of NCLV observed in our study compare with other data in the literature? Oechslin et al found a predominance of apical localization (about 95% of the cases), followed by involvement of the latero-medial and infero-median walls.17 Jenni et al found that non-compaction affected the latero-medial, apical and infero-median walls of the left ventricle.5 In a study of 32 adults, Sengupta et al found 100% of apical and lateral-median involvement. The lower wall was affected in 95% of cases.24 Steffel et al had identified a dilatation of the left atrium in 47% of cases and a dilation of the left ventricle in 36% of cases. These results are significantly lower than ours.23 Diagnostic delay in our series would explain this discrepancy. Left ventricular filling pressures were estimated to be high in 75% of cases. This was higher than the result found by Habib et al which reported elevated left ventricular filling pressures in 50% of patients.22
Although the diagnosis of NCLV is mainly based on echocardiography, there is still no consensus to date on the definition of non-compaction.25 Kohli et al 25 suggest that current echocardiographic diagnostic criteria are too sensitive and will result in many false positives of NCLV in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. This seems particularly true in black subjects.25 A high proportion of athletes fulfil the conventional criteria of NCLV without other phenotypic manifestations of the disease.26 The presence of left ventricular hypertrabeculation or even echocardiographic criteria of NCLV in isolation is probably not significant in the athlete.26 Left ventricular trabecular debris occurs in nearly 25% of pregnant women with complete regression after pregnancy in 69.2% of cases.27
MRI has become the method of choice for confirming or invalidating the diagnosis of NCLV. It remains a difficult procedure to access in our daily practice. It was only performed in one patient and did confirm the diagnosis.
The treatment of NCLV is identical to that of all cardiomyopathies, and depends on the clinical presentation of the patient. It is based on the management of complications such as heart failure, rhythm disorders and anticoagulation to prevent systemic embolisms.28 The prevention of thromboembolic complications has been the subject of debate. The thromboembolic risk of NCLV is well known and is frequently reported in adults.29 30 Thus, treatment with antiplatelet or oral anticoagulants should be considered, especially if there is atrial or ventricular dilatation or left ventricular systolic dysfunction.29 30 Ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias as well as bradyarrhythmias, most of which may be fatal, occur frequently in the case of NCLV.29
Device implantation (implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, resynchronization) and surgery (heart transplant) remain techniques that are not developed in our context or are too expensive to benefit our patients.
The mortality rate reported in the first series of cases was very high, but this rate appears to be decreasing in more recent series because of early diagnosis while the patient is asymptomatic. Ritter et al and Oechslin et al reported mortality rates of 35–47% during follow-up periods of 2.5 and 3.7 years, respectively.17 28 More recent publications indicating similar follow-up periods report a mortality rate ranging from 2–15%.31 We had seven deaths (20.6%). With an equal duration of follow-up, this result remains similar to the first series, which showed a high mortality rate. This could be explained by late diagnosis in our patients, especially those with NYHA functional class IV heart failure and high rate of decompensated heart failure.
Conclusion
Our series is the largest so far of NCLV in West Africa. Contrary to previous beliefs, NCLV may not be less common in black Africans than in other ethnic subgroups. Most of our patients presented in advanced stages of the disease. Clinicians in Africa should be made aware of NCLV so that it can be diagnosed at earlier stages.
Key messages
What is already known on this subject?
Non compaction of left ventricle (NCLV) is a rare congenital cardiomyopathy of recent description.
What does this study add?
NCLV may not be less common in black Africans.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
African clinicians should be aware of NCLV to avoid delayed diagnosis.
References
Footnotes
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent This was a retrospective study and the patients were not traceable at the time of the submission.
Ethics approval UCAD ethical committee for research.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.