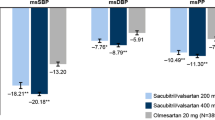
Abstract
The efficacy and acceptability of nebivolol 5 mg and enalapril 10 mg, each given once daily, were compared in essential hypertension in a multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial over 3 months. For the index pre-declared variable, sitting diastolic pressure at trough drug level, nebivolol achieved greater falls in pressure (−12.3 vs −9.9 mm Hg; P = 0.009) and a higher response rate (70% vs 55%; P = 0.002). The trough-to-peak sitting diastolic ratios also favoured nebivolol (84% vs 60%, P = 0.002). Nebivolol, but not enalapril, slightly but significantly lowered heart rate. Both drugs were well-tolerated, although enalapril was accompanied by a significantly higher incidence of coughing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Nueten, L., Schelling, A., Vertommen, C. et al. Nebivolol vs enalapril in the treatment of essential hypertension: a double-blind randomised trial. J Hum Hypertens 11, 813–819 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000550
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000550
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic Properties of Highly Selective β-blockers With or Without Additional Vasodilator Properties: Focus on Bisoprolol and Nebivolol in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy (2022)
-
Moderne vasoaktive Substanzen bevorzugt einsetzen
CardioVasc (2015)
-
Medikamentöse antihypertensive Therapie
Der Internist (2015)